Projects are also attractive because they represent a important source of revenue in value and in duration.
However, do not underestimate the risks associated with them, starting trade negotiations which shall incorporate a review of all binding contractual clauses for the buyer and seller.
Main risks to consider on Projects
- Insolvency of the buyer,
- Loss of funding during the project,
- Manufacturing risk: cancellation of the order while the seller has already begun to produce,
- Problems with third parties (stakeholders) that affect the entire project,
- Political risk (regime change, war ... etc.) including cases for export,
- Legal risk,
- Risk on guarantees granted to the buyer,
- Risk of low profitability,
- Currency risk, etc.
For example, if it is not so easy to assess the creditworthiness of a customer in the short term (3 months) for a sale of goods, it becomes extremely difficult to do it for a longer term (one year or more ...) for the simple reason that it is impossible to anticipate all the hazards inside and outside the company for such a period.
This reality concerns all risks on a case and it is further enhanced by the fact that the amounts involved in the business are often substantial.
This is why all of these risks must be carefully considered and balanced with security tools that are specific to each kind of risk:
- Contractual for legal risks,
- Payment means and payment guarantees for credit risk,
- Payment schedule for liquidity risk,
- Downpayments and / or insurances for the manufacturing risk (in case of cancellation of the project while it is in progress),
- Insurance for currency risk ... etc..
The purpose of this page is to provide operational tools to cover the "common core" of business on credit risk (risk of default), the manufacturing risk and liquidity risk.
Payment schedule
Negotiating the payment schedule is essential. Imagine "winning" a case of a 2-year period on which the seller would be paid only once the case is over. This would be catastrophic for the cash of the seller and would would incur costs during two years without money coming in the same time.It is therefore necessary to negotiate the terms of payments and billing throughout the case. Each term corresponds to a percentage of the amount of the case. More percentages are higher at the beginning of deal, the better for the seller's cash and risk management related thereto.
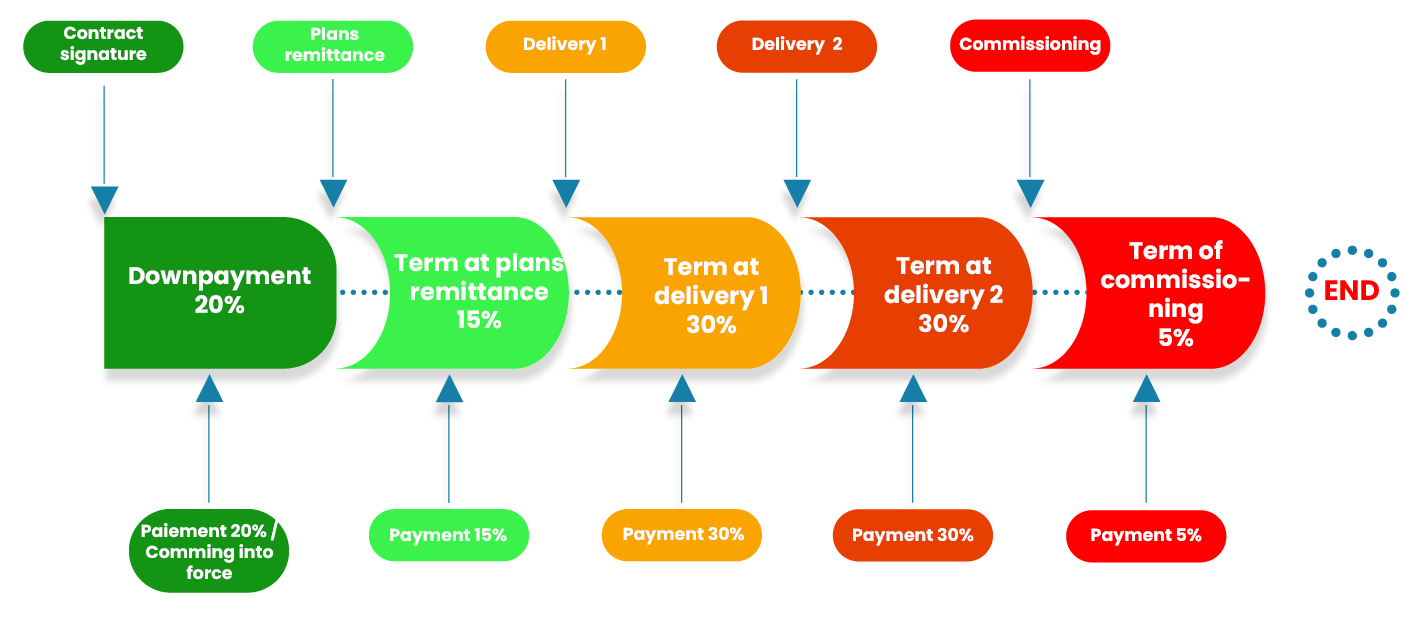
This payment schedule should be reconciled to the timing of costs that you will support the case. This is the purpose of the cash curve that highlights the impact of your business on the cash flow of your business.
It can be negative (costs are incurred before collected), neutral (the costs are offset by payments) or positive (the customer pays before you can stand the cost of the case).
-

How to manage Projects in My DSO Manager?
The flexibility of My DSO Manager makes it possible to adapt to any type of business, and allows qualitative monitoring and management of credit and political risk, as well as cash collection which are specific for big projects.
Internal Documents Management System allows to save and share all required documents to get paid by customers.
Clients can access to all information, statements, invoicies and documents on their own portal in My DSO Manager. See the online demo.
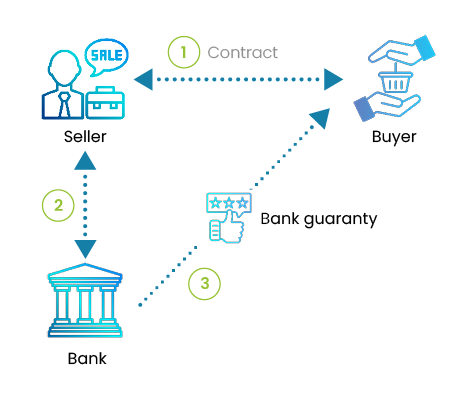
Bank guarantees in favor of the buyer
The buyer may require to the seller several types of bank guarantees on first demand or conditional to limit its own risks:- Bank Guarantee deposit: With this type of guarantee, the buyer may recover the full amount of the deposit paid at the beginning of deal if it finds that the seller has not fulfilled its obligations.
- Performance bank guarantee: protects the buyer against the risk of failure of the seller during the project.
- Bank guarantee of retention: it is common for the buyer to request a retention of guarantee. The payment is made less the amount of the guarantee retention (often between 5% and 10%). The resulting balance is paid at the expiration of the warranty period (usually 1 or 2 years).
It is more profitable for the seller to ask for a payment of 100% of the amount against a bank guarantee of retention that the purchaser will enable if necessary rather than waiting a year or two the payment in full of the invoices.
The bank guarantees on demand can be activated without any justification on the part of the buyer, even if the application is unfounded.
The conditional bank guarantees are activated only if the purchaser provides proof of the failure of the seller about at least one of the conditions included in the bank guarantee.
They pose less security for the buyer and less risk for the seller. Defining the conditions of the guarantee is very important because they have a direct impact on the ability of the buyer to enable it or not.
These bank guarantees also called market guarantees are "signature commitments" that engage the responsibility of the Seller. As such, the total amount of guarantees are included in the accounts "off balance sheet" of companies.
Bank guarantees in favor of the seller
Obtain a bank guarantee of payment or a standby letter of credit allows the seller to secure the insolvency risk of the purchaser.These tools can be difficult to obtain, but provide an effective security when the conditions of implementation are not restrictive and are issued and / or confirmed by a prime bank.
Prefer guarantees at first demand rather than guarantees containing conditions that require the seller to provide proof that the conditions mentioned in the warranty are met, otherwise the bank won't honor its commitment. If this is still the case (a conditional guarantee is chosen), the conditions must be analyzed closely because if they are too restrictive bank guarantee or standby L / C will have no value for the seller and won't provide him with a good security of payment.
Payment mean
Means of payment should be defined during negotiations and specified in the commercial contract.They have an impact on the risk of default (eg avoid paying by check). Some payment methods such as documentary credit also include a bank guarantee and secure the seller as the buyer.
Credit insurances
Insurances can cover many risks on business projects:- Credit risk: risk of insolvency of the buyer,
- Manufacturing risk: risk during the producing period before invoicing,
- Forex risk,
- Risk on bank guarantees in case of the default of the bank who issued them.
- Political risk in unstable countries...etc
Calculate the risk amount and its duration
To cover and mitigate the risks (credit, manufacturing, cash flow) of a case, the first step is to assess all the risks as accurately as possible.The following tools (cash curve and risks curves) can perform the calculation and allow to keep it update along the contract.
Indeed, it is common that the deadlines in the trade negotiations evolve during case progress. It is therefore necessary to monitor in real time the evolution of a case and its effects on the risks supported by your business.
Terms of suspension and termination
A contract binds the seller and the buyer of reciprocal obligations on the contract which can be long, up to several years. It is essential for the seller to set limits to its contractual obligations, especially in cases where the buyer does not comply with his.Suspension and termination clauses must be included in the contract to enable the seller to withdraw from its obligations if the buyer does not pay the bills and terms of the contract on their due date.
The advantage of these clauses is to clarify from commercial negotiations that the seller wants to be paid under the terms of the contract (payments, billing terms, payment period) and that he reserves the right to terminate it if is not the case.
The buyer has no reason to refuse these clauses because it would be a clear confession of his intention not to pay or delay payment from the terms of the contract.How to manage cash collection on Projects? The fundamental principles of cash collection always apply, even on complex projects. However, it is more technical, less automatable, and requires close monitoring of the collector, in phase with the progress of the project which may experience hazards during its execution phase.
Furthermore, the exigibility of a term or an invoice may be conditional on several elements. On a simple sale of a product or service, only the successful completion of the service or delivery of the product and the payment term define the due date. In the case of a project, the exigibility may contractually depend on many other points: certificates and attestations, commissioning, audit reports, etc.
For the collector, this involves ensuring that these conditions are met before following up with the customer, and being able to produce the relevant documents and attach them to the reminders.
In the event of late payments, the levers to get the customer to pay more pay are also more numerous, from an operational point of view as well as from a legal point of view when the contract includes suspension and/or penalty clauses in the event of unpaid debts.
The collection tool is therefore very important, centralizing all the information at your disposal, in a single place, and allowing interaction with all the players of the commercial relationship.